Table of Contents
- Chicken Pox Pictures Early Stages - HRF
- Does Chickenpox Still Exist 2024 - Elly Noelle
- #13: The success of chickenpox vaccines - by Saloni Dattani
- Case report: Hospital-acquired chickenpox in a healthcare setting ...
- GitHub - teofizzy/chicken_pox_case_count_prediction: using open source ...
- Incidences of chickenpox Germany | Statista
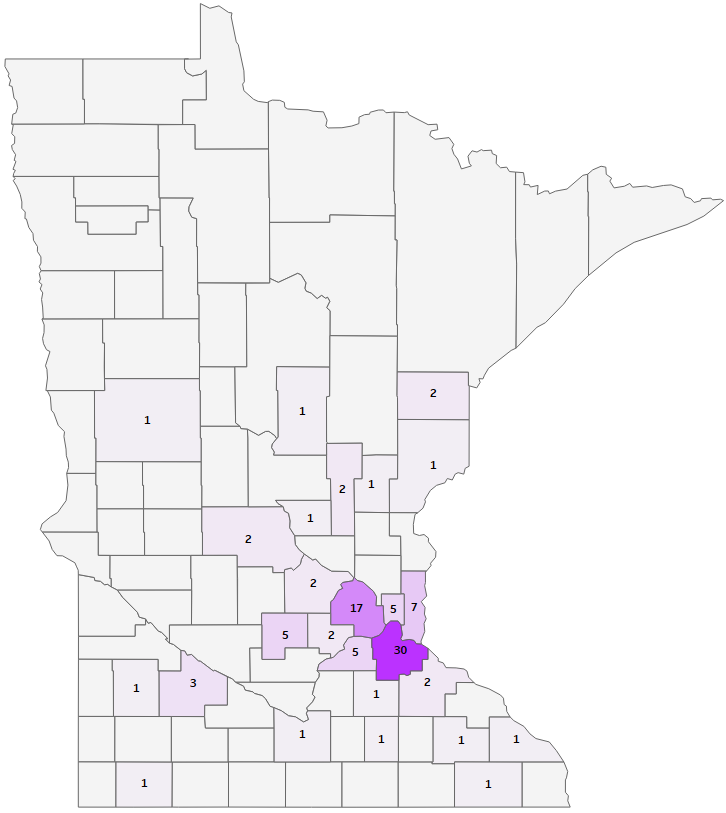
- Varicella (Chickenpox) and Zoster (Shingles) Statistics - MN Dept. of ...
- Varicella (Chickenpox) and Zoster (Shingles) Statistics - MN Dept. of ...
- Chickenpox cases by district fr | Download Scientific Diagram
- Why Are There Still Outbreaks of Chickenpox in the U.S.? – Chelsea’s ...

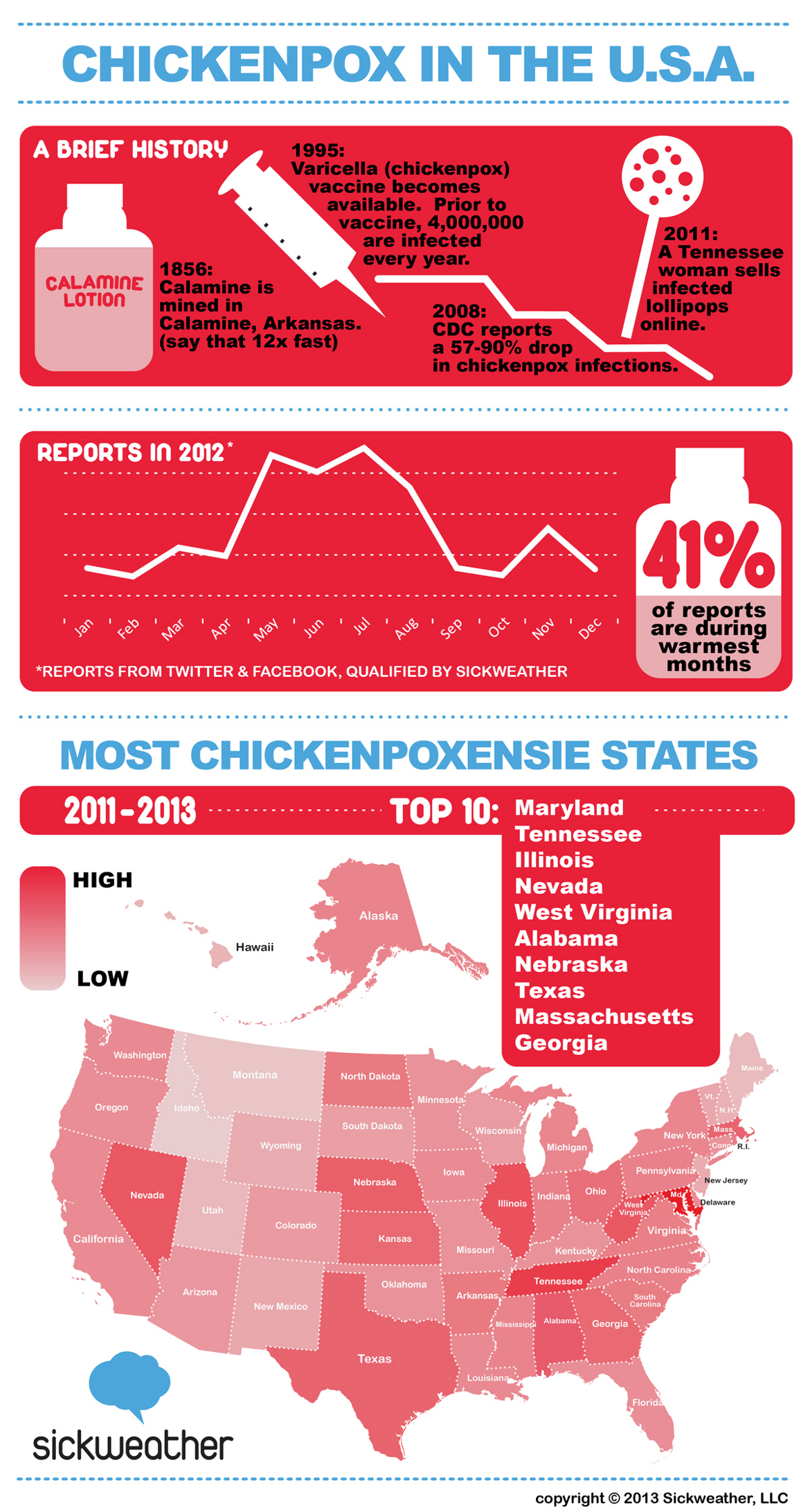
Varicella, commonly known as chickenpox, is a highly contagious illness caused by the varicella-zoster virus. According to the Minnesota Department of Health, chickenpox is a common childhood disease that can have serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of varicella, exploring its symptoms, transmission, treatment, and prevention methods.
Symptoms of Varicella

The symptoms of chickenpox typically appear within 10 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. The most common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Rash, which progresses from red bumps to blisters and eventually crusts over

It's essential to note that some people may experience more severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or confusion. If you or your child is experiencing any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.

Transmission of Varicella

Chickenpox is highly contagious and can spread through:
- Airborne transmission, such as coughing or sneezing
- Direct contact with an infected person's rash
- Contaminated surfaces or objects
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with cancer or taking immunosuppressive medications, are more susceptible to contracting chickenpox.

Treatment and Prevention of Varicella
While there is no cure for chickenpox, treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. These include:
- Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms
- Pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to manage fever and discomfort
- Calamine lotion or oatmeal baths to soothe the rash
To prevent the spread of chickenpox, the Minnesota Department of Health recommends:
- Vaccination: The varicella vaccine is a safe and effective way to prevent chickenpox. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend two doses of the vaccine, typically administered at 12 to 15 months and 4 to 6 years of age.
- Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals
- Staying home from school or work if you or your child has chickenpox
Varicella, or chickenpox, is a common childhood illness that can have serious complications if left untreated. By understanding the symptoms, transmission, treatment, and prevention methods of chickenpox, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Remember to stay informed, stay vigilant, and consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns about varicella. For more information, visit the Minnesota Department of Health website.
Keyword: Varicella, Chickenpox, MN Dept. of Health